-40%
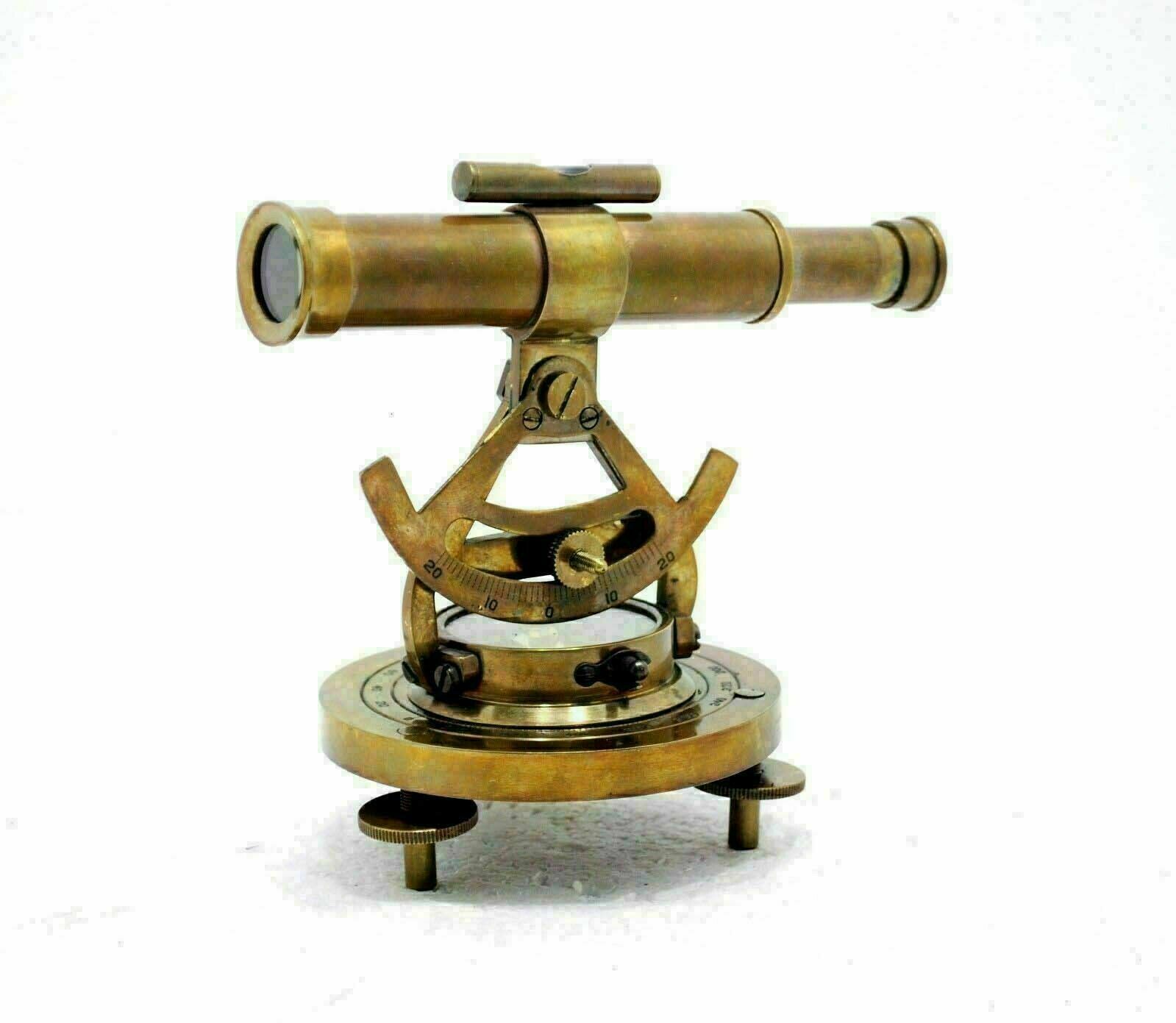
Unusual 1915 Ainsworth Mining Transit Box 3 Screw Level Base Odd Verniers
$ 488.4
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
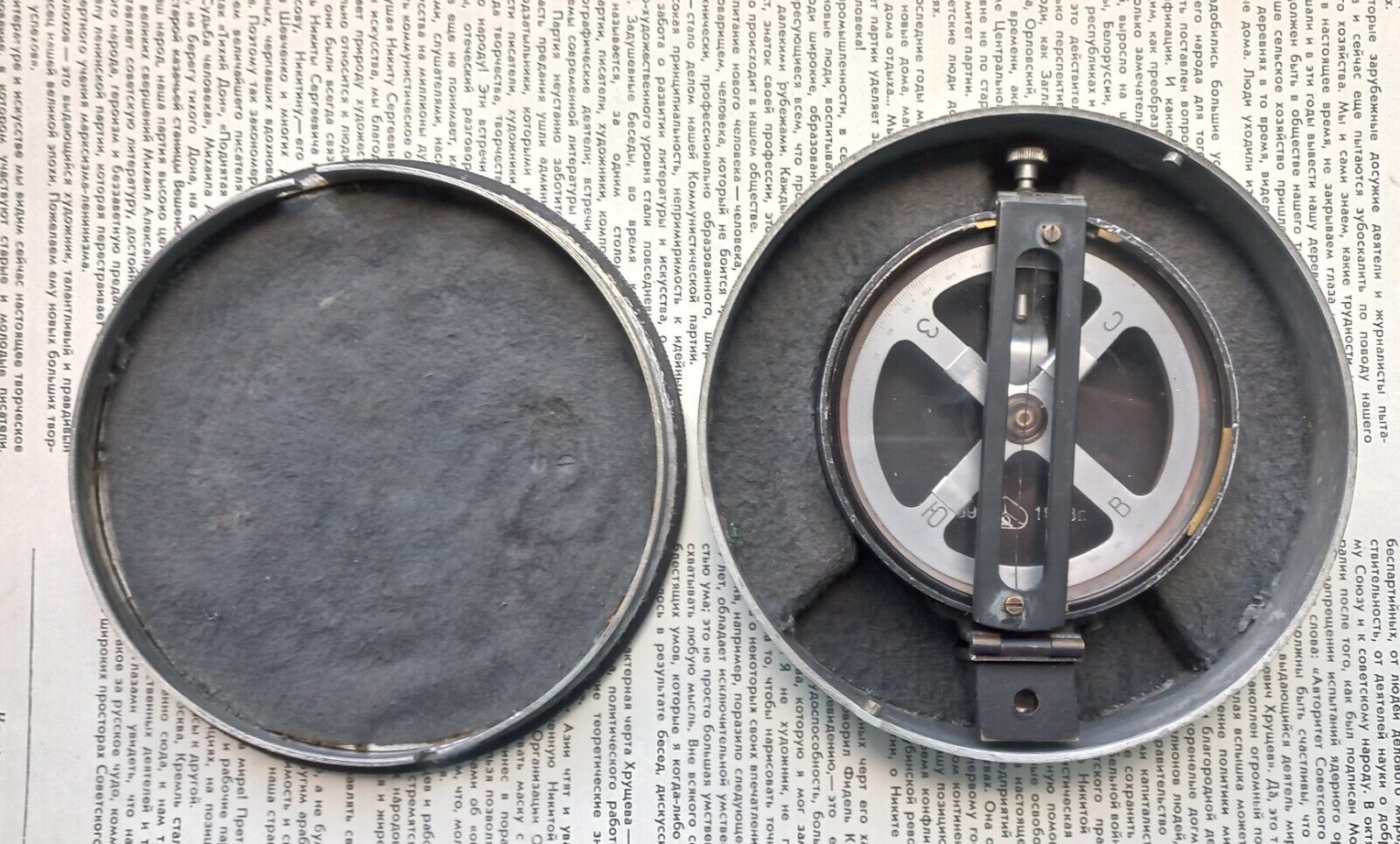
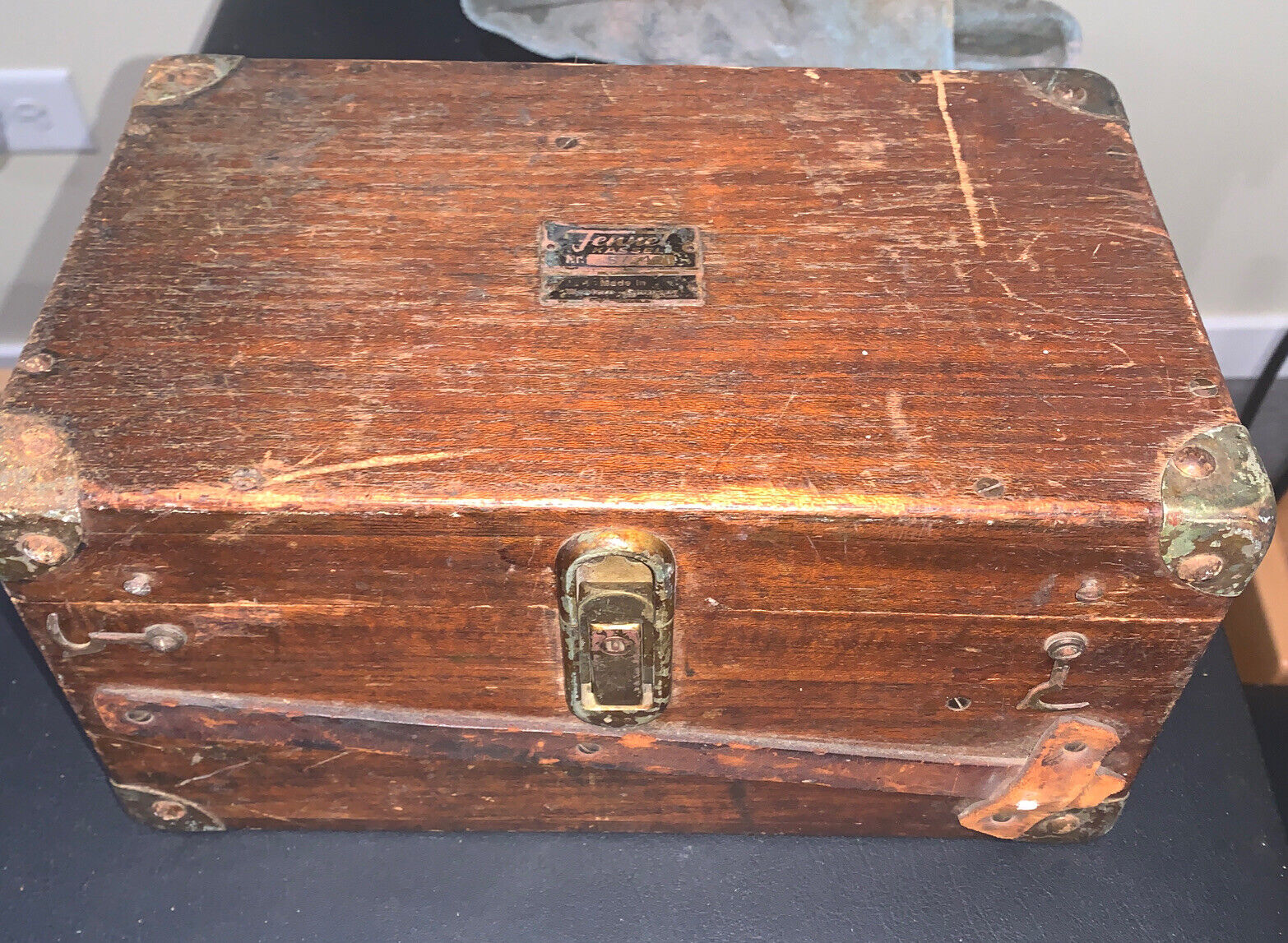
This is very unusual Ainsworth mining transit I have had in my collection for 30 years, I don't think it ever had an auxiliary mining scope but it is set up for one. It has an opposing Vernier that I am not even certain how to read so not even sure how precise it is? It also has a very unusual 3 screw level base that seems far better made than the standard 4 screw base. Motions are smooth, optics and 3 wire cross hairs are in good shape, this is a good working instrument with the wood box and a few box extras. This transit has an 10" long scope, a 2 1/2" compass needle and a 5" plate. There are some not very noticeable scratches in the finish on top of the scope near the eyepiece end, not terrible otherwise the finish on it is great. The box is a Dietzgen box but is sure a good fit for this transit.Postage is .00 if within the US, more If you are outside the US; no charge for careful packing.
Here is some information on the well known Denver Maker Ainsworth firm:
William Ainsworth
William Ainsworth was the founder of the Wm. Ainsworth Company which was in existence in Denver, Colorado, from 1880 through 1905. The name was changed to Wm. Ainsworth and Sons in 1905 with the inclusion of his sons Robert and Alfred.
The success of the Brunton Pocket Transit may have contributed to the decision of Ainsworth Company to build and market surveying instruments. In any event, the work was started on surveying instruments around 1903 or 1904, but the first transits were not marketed until 1906. This continued until 1940, when the transit business was sold to Harry Glantz, who had been an instrument maker for Ainsworth.
William Ainsworth immigrated to American at the age of 3 in the year 1853. As a young man he became a master watchmaker for the Elgin Watch Company. In 1874 he settled in Central City, Colorado, where he became recognized as a specialist watch repairman; repairing complicated Swiss repeater watches. His repair skills brought him close to the circles associated with mine assaying, repairing the many English-made precision balances. This association, and his knowledge of fine machine work soon developed into the production of precision balances. Ainsworth's first balance was built in 1879. The company's products soon became the standard for Assayers.
Sometime during the late 19th Century, William Ainsworth Company began the manufacture of fine surveying instruments. A 1905 Wm. Ainsworth & Sons catalogue states that his familiarity to the watch making trade,... "which is unequaled by any industry in the world for systematic accuracy, factory methods and results"... has prepared his company to produce the finest of instruments. In 1907 the company built a precision circular dividing engine.
On September 18th, 1894, D. W. Brunton was granted a patent for his "Pocket Transit". Brunton devised the combination instrument to serve for the necessary survey work required for commercial and legal mine-examinations. The sole manufacturer for the patent instrument was the Wm. Ainsworth Company. Brunton states in an account dated 1905, that the instrument was in use, "from Australia to Alaska". He also notes that the instruction of the instrument was taught at ... "Lawrence Scientific School, Harvard University, Columbia University, and a number of western mining schools'. At that time, neither Brunton or Ainsworth could have realized, that the success of the combination instrument was only just beginning to realize its potential; to date, almost 100 years of production and use. William Ainsworth died on January 1st, 1917. The company of Wm. Ainsworth & Sons continued the manufacture of Surveying instruments until 1938.
William Ainsworth
William Ainsworth was the founder of the Wm. Ainsworth Company which was in existence in Denver, Colorado, from 1880 through 1905. The name was changed to Wm. Ainsworth and Sons in 1905 with the inclusion of his sons Robert and Alfred.
The success of the Brunton Pocket Transit may have contributed to the decision of Ainsworth Company to build and market surveying instruments. In any event, the work was started on surveying instruments around 1903 or 1904, but the first transits were not marketed until 1906. This continued until 1940, when the transit business was sold to Harry Glantz, who had been an instrument maker for Ainsworth.
Development of the manufacture of assay balances in the western states begins with the company of William Ainsworth.
Ainsworth, the founder of William Ainsworth & Sons, Inc., was born January 22, 1850, in Lancashire, England. He, his mother and a sister Anne Elizabeth (born May 1842) came to America in 1853, but for reasons not known, he and his sister were soon was left orphans. Regardless of the circumstance that brought this about, William was left in the care of George and Suzanne Elliott an English family owning a farm near Sussex, Wisconsin. His sister was left with the Charles Hart family in nearby Brookfield. In order to pay for his food and lodging William performed farm chores.
Ainsworth's particular passion, even as a small boy and continuing through the rest of his life, was for steam engines, although he seemed to have an affinity for all types of mechanical apparatuses. One story that he often told gives us some insight into his abilities: Arrival in his neighborhood of the first grain binder caused great excitement on the farms in the area. Unfortunately, the owners had no idea how to assemble it, so they sent for Ainsworth. After studying the parts carefully, he began the complicated job of assembly. Once he had finished the job, they hooked the machine up and it worked perfectly. In his early teens, after completing an apprenticeship with a clockmaker, he went into business on his own repairing clocks. In order to sell his "service" he would travel through an area playing his guitar to attract a crowd. In between songs, he would get in a plug for his clock repair.
Still in his teens, he obtained a job in the Elgin watch factory at Elgin, Illinois. The exact details of his work with Elgin are rather obscure, but it is known that one of his duties was that of a "springer". This consisted of selecting, testing, installing and manipulating the hair springs of the watches, a very delicate and tedious job.
Although the record is not definite, we do know Ainsworth worked for a period of time for the Union Copper Distilling Company of Calumet in Cook County, Illinois. (The company made and distributed bourbon, rye whisky, 188 proof alcohol, cologne spirits and French neutral spirits). Here he was employed as a steam engineer and family stories indicate his employers were so impressed by his mechanical ability that in a very short time, he was made Chief Engineer. He must have stayed with this job for several years and in February of 1874, at the age of 24, requested and received a letter of recommendation. (He also received an August 18, 1875 letter of recommendation from the Office of Roelle, Junker & Company, Distillers & Rectifiers located at 261 & 263 East Kinzie, corner Cass St. in Chicago. This letter was signed by the secretary of Union Copper Distilling Company located in Riverdale, Illinois).
He next moved to Black River Falls, Wisconsin, where for a short time he worked for J. W. Cole and Company (Drugs, Paints, Oils and Fine Liquors) as a watch maker. During his time with Cole and Company, he worked with W. B. Woolsey, another watch maker whom he had met and worked with at the National Watch Factory in Elgin. Mr. Woolsey in his letter of recommendation states, ". . . he is the best man on the lathe that I ever saw in short he thoroughly understands a watch in every respect." It was also in Black River Falls that he met Elma E. Eastman, a young girl from New York who had arrived in Wisconsin to visit a sister. The Denver Post of January 2, 1917 leads to the belief that Ainsworth and Elma Eastman were married in Minneapolis, Minnesota. He remained in the employ of the Cole Company possibly through September of 1875.
It is evident that through the preceding experiences, Ainsworth learned to be top-notch toolmaker and mechanical engineer. In later years, evidence of his designing and tool-making ability could be found around the Ainsworth factory in Denver in the tools which he built for the manufacture of the early balances. Some of these tools were still in use in the factory as late as 1965 and the family of his grandson, Robert Ainsworth, still has one of the original lathes built from "scratch" by Ainsworth sometime prior to 1900.
In 1875 or 1876, the young couple came west, traveled through Denver and settled in Central City, Colorado. Upon his arrival in Central City, he turned to his watchmaking trade to earn a living and worked for various jewelers there. He soon developed a specialty cleaning and repairing Swiss Repeater watches, a very fine handmade Swiss watch which struck the hours, half-hours, and quarter-hours.
This work led Ainsworth into contact with a variety of people, mostly miners and assayers, and it is believed that these associations eventually led him into the balance business. One source indicates that Richard Pearce, Nathaniel Hill's head metallurgist at the Boston and Colorado Smelter, one day needed an assay balance fixed and in order to avoid sending it back to England for repair, presented it to Ainsworth and suggested he try his hand at repairing it. In those days, Oertling, Becker and Troemner balances were shipped from their factories in England, Philadelphia and New York. When these balances would not function properly, they had to be returned to those cities, which constituted a wait of many months. Consequently, Ainsworth, in order to help the assayers, began repairing the assay balances and in time learned the "secrets of the trade." He determined that since assay balances were in great demand at that time, they could be made just as well in Colorado as in England, Philadelphia or New York and he proceeded to develop his ideas for manufacturing them.
In the meantime, Ainsworth and his wife cultivated a business of making decorative chains from the native silver being produced from the mines in the area and indications are that, at least for a short time, those chains were the height of fashion in the socially prominent Central City.
In 1877 the Ainsworths moved to Denver, probably to be closer to suppliers of materials he needed for making balances and to try to make more of his abilities as a watchmaker, repairman and machinist and his newly developed expertise in time lock repairing for banks. Although his primary sources of income were watchmaking, machining and time lock repairing for banks, he continued to develop his balance trade on the side. The Denver City Directory of 1879 lists William Ainsworth as a watchmaker for A. B. Ingols Jewelry and in 1880 and 1881 he is listed as an owner in the Swain & Ainsworth Machine Shop on 474 Larimer Street.
It was in 1879 while serving as a watchmaker for A. B. Ingols that Ainsworth probably made his first balance. He began by buying a small hand planer and on this planer he machined the bed of a small engine lathe. He built the lathe in its entirety and then began the slow process of making his own taps and dies. He established his own standards of sizes and thread forms. It is also believed that he then constructed a milling machine.
The first balance parts were turned out on the small lathe and miller with a great deal of hand work. The brass beams were laid out and sawed with a jeweler's saw and the balance cases were made of high grade African mahogany with a French polish finish.
In 1882 Ainsworth had his watchmaking and balance shop at 248 16th Street. Several years later he located his "Watchmaker and Mane'g Jeweler" shop at 577 and 579 Lawrence St. This address eventually became his factory and home for many years. In 1887 a street re-numbering occurred and, although the factory and home remained in the same bulding at the same location, the address became 2151 Lawrence.
Information regarding Ainsworth's early balances is, of course, quite scarce. A serial number record from #473 to #2027 is known, but it only provides a description; there are no dates. One assay balance is known with a number 090 inscribed on the beam. 090 doesn't fit any of numbers of the various models of balances built by Ainsworth, nor does it fit part numbers which were used from time to time and were two digit numbers. Since Ainsworth gained much of his early training in watch repairing where almost everything has a serial number, it is believed he may have begun his numbering system with 001. It is possible to date balance number 1000 at 1898, which would mean that Ainsworth built one thousand balances between 1880 and 1898. This works out that the company built approximately 50 balances a year. Since in 1899 the company built approximately 100 balances, 50 a year does not seem unlikely. Balance number 2027 was made in 1902, but unfortunately, there is a large gap in serial number information between 1902 and 1945.
Since there were no balance theory and design textbooks available to Ainsworth, he made use of the experience and practice of other balance manufacturers. Drawing on the work of Paul Bunge of Hamburg, who in 1866 had proved a shorter beam in a balance does not necessarily mean less accuracy, Ainsworth began his own experiments with a short balance beam.
One of Ainsworth's outstanding contributions to the industry were these experiments in shortening the balance beam, which effectivly quickened the assaying process. (The shorter the beam, the faster the oscillations). The early Oertling and early Ainsworth balances had beams as long as 10". Extremely long beams were used in the early days because the adjustment of the knife edges did not need to be as accurate on a long beam as they have to be on shorter ones; therefore, adjustments were much easier. They were, however, very slow in their oscillations. Balances were manufactured in the Ainsworth plant having beams only 4 inches long and possibly a few of only 3 1/2 inches. It was learned from these early balances that the very short beams are not as dependable and stable as the five-inch length which was eventually adopted as a standard, although as late as 1920 both 4-inch and 6-inch beams were available.
It has been determined reasonably accurately that balance manufacturing, as well as the firm of William Ainsworth Balance Company, started in 1880 even though he continued with his watch repair and time lock service. In that year the personnel in the Ainsworth factory located at 348 16th Street (only a few doors from where Ainsworth worked as a watchmaker), consisted of William Ainsworth, an apprentice, a cabinet maker, and a mechanic. Again the wood of choice was mahogany; a former employee of the Ainsworth Company has stated that the mahogany used in the company's balances came from the Gold Coast (Ghana) of Africa.
Ainsworth balances were almost immediately preferred by the local assayers. In spite of this acceptance, however, the problem of building sufficient volume to support a family with this infant industry was a tough one and Ainsworth found it necessary to hire out his services to keep the business going. It may be this situation that caused him to be listed as a watchmaker and machinist rather than a balance maker.
It was also in the 1880s that he became well-known for his ability to clean and repair time locks in bank vaults, and he developed a good business maintaining the time locks in all the leading banks of Denver and the surrounding area. There is one story from the family that is well worth telling, for it shows us something of the character of William Ainworth. ". . . . a certain store manager engaged Ainsworth to clean and repair his safe and then refused to pay the mechanic his fee. Ainsworth quietly returned to the safe and performed an operation that later proved one of the most effective collective agencies devised by man. Several hours later the owner accosted Ainsworth and complained that he could not open his safe. 'I know you can't', Ainsworth replied amiably. 'Well, what's wrong?' the merchant wanted to know. Ainsworth, still amiably, replied that he had changed the combination. When the angry owner demanded the new combination, Ainsworth bargained, 'Pay me what you owe me and you'll get your combination'. Well, Bill Ainsworth got his money and the owner got his combination."
As was the case in the eastern United States of Voland, Van Zelm, Kohlbusch (and perhaps to a certain extent Troemner) working for Becker before they went out on their own, so it was in the west that William Ainsworth provided the experience and perhaps the motivation for a number of prospective balance manufacturers. Of the five prominent western balance companies, all but one of the owners had at least some part of their training with William Ainsworth. They were Elmer Smith and Fred Thompson who would establish Smith & Thompson Balance Company (later to become the Thompson Balance Company), Albert Dahlberg and Hugo Franow who would establish the Denver Balance Company, and George Keller who would establish the Keller Balance Comany in Salt Lake City. The latter gave some training and opportunity to George Spiegel and Wilfred Huesser in their balance making endeavors.
The Ainsworth Balance Company survived the panic of 1893, possibly due to the outside work of William Ainsworth in repairing clocks, watches, safes, etc.
On September 18th, 1894, D. W. Brunton was granted a patent for his "Pocket Transit". Brunton devised the combination instrument to serve for the necessary survey work required for commercial and legal mine-examinations.
Sometime around 1894 or 1895, Mr. D. W. Brunton brought his newly patented Brunton Pocket Transit to William Ainsworth to manufacture. The first lot consisted of twenty-five instruments, and thus began the Brunton Pocket Transit business. The
Wm. Ainsworth Company
was t
he sole manufacturer for the patent instrument
which was to serve the company well into the 20th century.
Brunton states in an account dated 1905, that the instrument was in use, "from Australia to Alaska". He also notes that the instruction of the instrument was taught at ... "Lawrence Scientific School, Harvard University, Columbia University, and a number of western mining schools'. At that time, neither Brunton or Ainsworth could have realized, that the success of the combination instrument was only just beginning to realize its potential; to date, almost 100 years of production and use.
The success of the Brunton Pocket Transit may have contributed to the decision of Ainsworth Company to build and market surveying instruments.
Sometime during the late 19th Century, William Ainsworth Company began the manufacture of fine surveying instruments. A 1905 Wm. Ainsworth & Sons catalogue states that his familiarity to the watch making trade,... "which is unequaled by any industry in the world for systematic accuracy, factory methods and results"... has prepared his company to produce the finest of instruments.
In any event, the work was started on surveying instruments around 1903 or 1904, but the first transits were not marketed until 1906.
In 1907 the company built a precision circular dividing engine.
This continued until 1940, when the transit business was sold to Harry Glantz, who had been an instrument maker for Ainsworth. After that purchase, the transit business that had operated under the Ainsworth name became known as Rocky Mountain Instrument Company. Harry Glantz died around 1945 and his son Omar took over the business. The company was last listed in the Denver Business Directory of 1955.
The Ainsworth Balance Company continued to grow and prosper and around 1899, William's two sons joined him and the company became known as Ainsworth and Sons. Robert G. Ainsworth was born in Pennsylvania on January 1, 1878 and Alfred W. Ainsworth on October 30, 1884. Both got their early training in the Ainsworth factory and it was a natural course of events that led them to join the firm in 1899.
Some of the problems inherent in the assay balances of this time was the handling of the rider. The rider was a small "inverted V" shaped platinum weight that was placed at various indexes along the beam to subdivide the weight placed in the pan below. It gave the operator a much more accurate weighing with a minimum of handling of the larger gram weights used in the pans. The assayer, however, was limited to the weight of a particular rider and if he wanted to change that rider, he had to open the case and very carefully replace one rider with another.
To handle this problem, the idea of the multiple rider was developed. With a multiple rider attachment, the operator no longer had to open the case to change weights; he merely turned a rod and replaced one rider weight with another. It has been claimed that the Ainsworth Company was the first to develop and patent a multiple rider carrier; however, the records of the U. S. Patent office reveal that Fred W. Thompson filed his patent for a multiple rider carrier on December 26, 1903 (patent no. 768,829) while Robert G. Ainsworth filed his patent on May 8, 1905. The two multiple rider carrier ideas were different in design, but achieved the same goal.
Sometime around 1910, Ainsworth & Sons began a major shift from manufacturing assay balances to manufacturing analytical balances. These had been made and sold prior to this time, but not in any great number. The change in emphasis was probably due to several reasons: a general decline in mining, the fact that assaying was more often done in a central assay office rather than many separate assay offices, and the fact that the demand for general scientific research was increasing the demand for more and better analytical balances. This production and development eventually led to Ainsworth's first micro-balances. Balances were developed that would weigh in a vacuum and under pressure, that would show the loss of weight of a drop of alcohol as it evaporated, that would register the difference in weight created by the a sunbeam striking a piece of paper or the weight of a pencil line on a piece of paper.
Around 1916, the company began receiving orders for balances, weights, Bruntons, etc., due to the preparation for World War I.
William Ainsworth died January 1, 1917, leaving the management of the company in the hands of his two sons and his wife, Elma E. Ainsworth. From 1918 until the 1930s the company went through a period of wide diversification. These included manufacture of a Dodge automobile transmission, spotlights, tire gauges, automobile signaling devices, perfume atomizers, toilet flush valves, moving picture machines, smoking pipes, furnace grates, valve-facing tools for automobiles, seismographs, mining carbide lamps, gunsights, and radio parts. By 1934 the idea of wooden cased balances was abandoned and the Company began producing balances in metal cases.
The Ainsworth and Sons Company was purchased in 1965 by Xavier Science Corporation, and in 1967 the plant was moved to the Denver Tech Center. During this time, ownership of the company went through several hands, including Tastee-Freeze Industries, Inc. of Chicago. More recently, the rights to the Ainsworth name have been purchased by the Denver Instrument Company of Denver.
Catalogue Listings
The first appearance of an Ainsworth assay balance that has been found occurred in the Denver Fire Clay catalogue of 1895. Although the company was producing at least eight different models by this time, they were only represented in this catalogue with the model 043 and 045. The No. 043 used agate in both the knives and bearings and also contained double rider arms.
By 1898, Denver Fire Clay had added an Ainsworth No. 044 and a No. 1 with the option of different sensibilities and different beam lengths. They also added a page of descriptions of some of the improvements that had been made by Ainsworth, which was probably a conscious effort to draw more attention to this local company rather than Oertling, Troemner and Becker.
With their 1901 catalogue, DFC listed eight styles of Ainsworth assay balances : No. 0, 1 (three models), 043, 044 (two models), and 045 (two models); this offering was continued at least until 1923 when their catalogue was still offering the same selection.
Henry Heil in 1904 had realized the marketability of Ainsworth balances and offered seven models to buyers.
In 1905 Ainsworth made many design changes, changed the model numbers of his balances and introduced his multiple rider carrier. These same models were again shown in their 1909 catalogue.
An inverted beam assay balance had been added to the inventory by 1911, and by 1912 MASSCO was listing thirteen models, including a portable. In 1916, the Justinian Caire catalogue had added the Ainsworth line with six models, including a slant-front portable. The popularity of the inverted beam assay balance was apparent, as it was offered by Braun in 1925 and by MASSCO in 1929.
An important milestone in the development of assay balances occurred sometime around 1934. The DFC catalogue for that year offered two inverted beam assay balance models, the V and VM, in aluminum cases.
By 1940, Ainsworth catalogues reflected the change in the balance industry by offering only three assay balances out of a total nineteen balances offered. Except for those three, the balances were analytical of varying degrees of sensibility, including one micro-balance. This marked the end of the era of the French polished mahogany cases with finely machined gold lacquered brass parts.